Exercise sheet 8: Data Driven Life Sciences
Exercise 1
1a)
Arrange the following terms into their correct order in the Illumina sequencing method and describe each of them briefly:
bridge amplification
deblocking
library preparation
annealing of template strands to flow cell
fluorescence detection
Hide
Solution
1. Library preparation:
A sequencing library gets prepared from a sample by fragmenting the original DNA and adding Illumina-specific adapter sequences to both ends of the fragments. The library is what gets read during sequencing.
2. Template strand annealing
The single-stranded library fragments are used as template strands in the sequencing and are annealed to primer sequences, which are bound to the flow cell and are complementary to the adapter sequences of the fragments.
3. Bridge amplification
After complementary strands have been synthesized and the templates been washed off, the now flow cell-bound fragments are amplified in several cycles of so-called bridge-amplification to form fragment colonies, or clusters on the flow cell to guarantee a detectable fluorescence signal during sequencing.
4. Fluorescence detection
Illumina-sequencing is a form of sequencing-by-synthesis in which the nucleotides incorporated into the growing strand are detected via attached fluorophores. After the first \(3\) steps, the following steps are iterated to sequence the entire read:
Modified nucleotides, containing a fluorescent group, are used to extend the strand, their blocking groups are cleaved from their 3`-OH groups.
5. Deblocking
Deblocking is the removal of the fluorophore (blocking group). It is necessary before a new round of elongation by one nucleotide can begin.
More information about this topic can be found on the Illumina Webpage.
Exercise 2
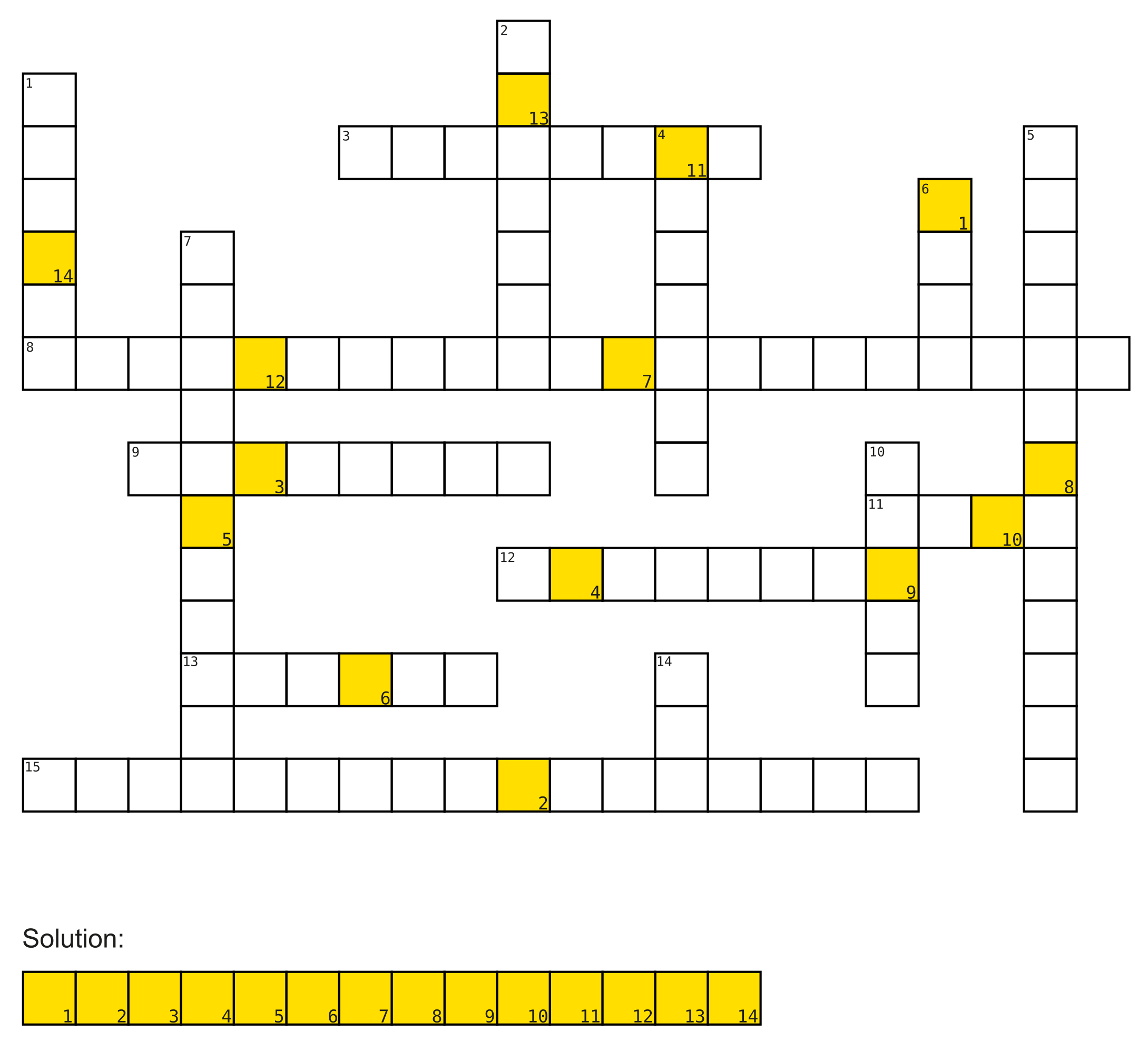
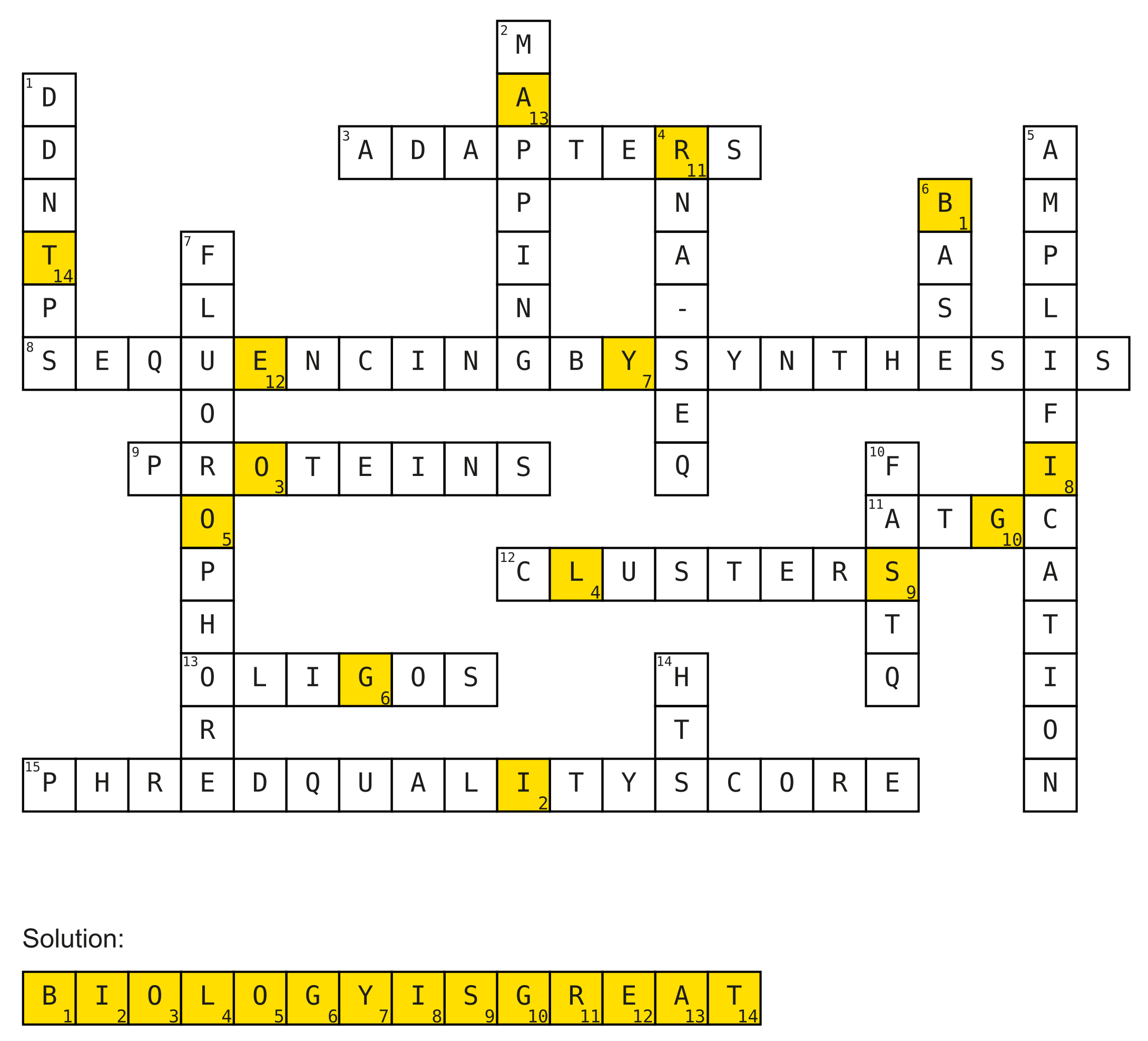
2a)
Solve the crossword puzzle!
Horizontal:
- Added to DNA fragments during library preparation.
- Illumina way of determining the order of nucleotides in a DNA strand. (3 words)
- ChIP-Seq can be used for sequencing DNA regions that are bound by these.
- The alphabet of life.
- Formed by bridge-amplification on Illumina flow-cells.
- Flowcell surface filled with these 2 different DNA molecules.
- Measure to asses the quality of the identification of nucleobases generated by automated DNA sequencing. (3 words)
Vertical:
- Dideoxynucleosidetriphosphates (abbrev.)
- Process of determining positions of reads on the reference genome.
- Gene expression can be measured using this. (abbrev. hyph.)
- The process of making many copies of a piece of DNA.
- Found in pairs in DNA.
- Chemical group attached to nucleotides to monitor incorporation into DNA.
- File format used to store sequence information.
- Breakthrough sequencing method (abbrev.)
Hide
Solution
Exercise 3
3a)
You want to determine how many reads \(N\) are needed to achieve a coverage depth \(C\) of 20X when sequencing reads for Escherichia coli.
The length of the reads \(L\) is 30nt and the E. coli genome \(G\) is approximately 4.6 million bases long.
Hide
Formula
\[ N = \frac{C\times G}{L} \]
Solution
\[ N = \frac{20\times 4600000}{30} \approx 3066667 \text{ reads} \]